Quick Summary → Hypnosis for childhood trauma helps process emotions, reframe negative beliefs, and reduce symptoms like anxiety and flashbacks. Techniques like guided imagery and positive suggestions promote healing and self-esteem. It empowers you to regain control and move forward.
1 in 7 children have experience child abuse or neglect… if you’re reading this there’s a pretty good chance that you may be may also be suffering from a childhood trauma.
There are a lot of uncomfortable symptoms you may experience, such as:
- Inability to lose weight
- Fear
- Stress
- Anxiety
- Nightmares
(the good news is that here’s a way to eliminate all of these issues!)
In this post, you’ll learn how hypnosis can reduce or eliminate childhood trauma, how long it takes to heal, and how to get started right now.
What Is a Childhood Trauma?
A childhood trauma is a trauma caused by a negative or extreme experience from the past – usually it’s a frightening, dangerous, or violent experience.
The effects of childhood trauma can last from a couple of hours to a lifetime.

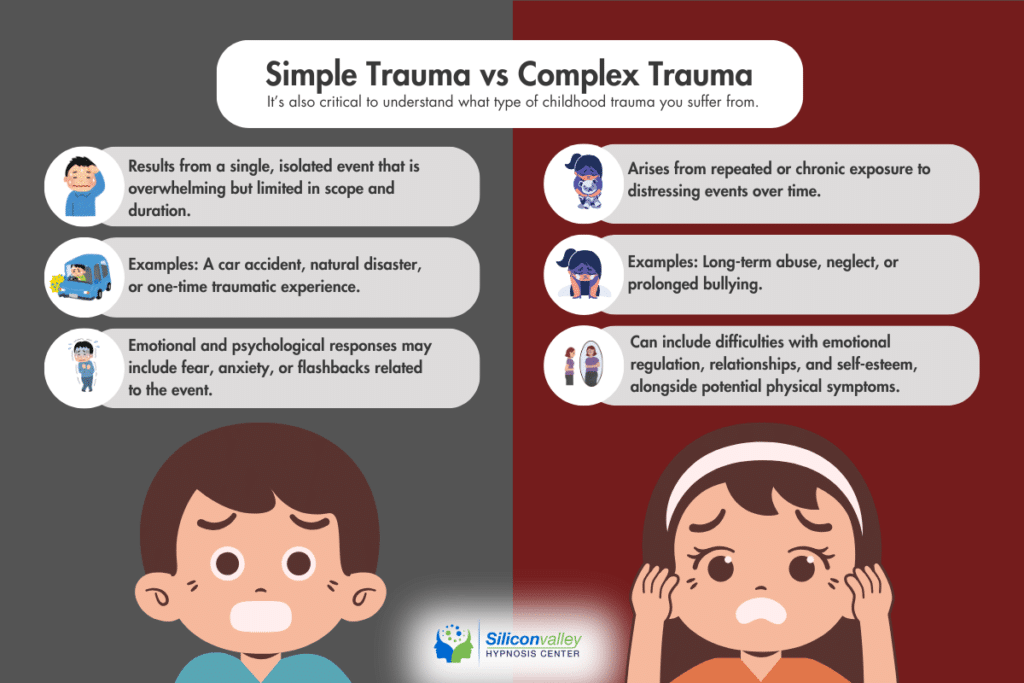
Simple Trauma vs. Complex Trauma
It’s also critical to understand what type of childhood trauma you suffer from.
- Simple trauma. It usually results from a single, isolated event that is overwhelming, but limited in scope and duration (e.g. a car accident, natural disaster, one-time experience).
- Complex trauma. It usually results from a repeated or chronic exposure to distressing events (e.g. ongoing abuse, neglect, prolonged bullying).
It’s critical you understand the difference – and know what type of trauma you suffer from.
Each type of trauma has its own characteristics, impact, and recovery tactics, which is critical to helping you resolve your trauma as soon as possible.
Childhood Trauma Test: Free Quiz
Here’s a free childhood trauma quiz to find out whether you suffer from a childhood trauma. This quiz is not intended to provide a diagnosis – that is for a psychologist, therapist, or psychiatrist to do. It is meant to provide insight for you.
For each question, look back in the past on whether it’s correct before you were 18.
- If it occurred often or significantly impacted you, mark it as Yes.
- If it did not happen, or happened very rarely, mark it as No.
Family Environment
- Did a parent or adult in the household often yell at you, insult you, or put you down?
- Did a parent or adult in the household physically harm you (push, slap, hit, or throw something at you)?
- Did you often feel that no one in your family loved you or thought you were important or special?
- Did you often feel that your family didn’t look out for each other, feel close to each other, or support each other?
Abuse and Neglect
- Did you often feel unsafe in your home, or were you exposed to violent environments?
- Did you go without clean clothes, food, or basic needs because your family couldn’t afford them?
- Were you emotionally neglected (your feelings, needs, or presence ignored)?
Parental Behavior and Structure
- Did you live with someone who had a problem with alcohol, drugs, or another addiction?
- Did you live with a family member who was depressed, mentally ill, or attempted suicide?
- Was a parent or caregiver absent due to separation, divorce, or imprisonment?
External Trauma and Social Factors:
- Did you witness physical violence between parents or other adults in your home?
- Were you ever bullied or socially isolated at school or in your community?
- Were you ever sexually abused or touched inappropriately by an adult or older child?
Looking for the Results?
Count each time you’ve answered “Yes” to a question.
The higher the number, the more adverse childhood experiences you may have faced, which could potentially impact your mental, emotional, and physical well-being.
NOTE: You can also get this done with childhood trauma test pictures.
10 Most Common Signs of Childhood Trauma
Here are the most common symptoms of childhood trauma:
- Emotional Dysregulation. Struggling to manage emotions, leading to frequent outbursts or shutting down during stressful situations.
- Hypervigilance. Constantly feeling on edge, scanning for threats, or expecting danger even in safe environments.
- Trust Issues. Difficulty trusting others or forming close relationships due to fear of betrayal or abandonment.
- Attachment Problems. Experiencing overly clingy behavior, fear of rejection, or difficulty forming healthy bonds.
- Low Self-Esteem. Persistent feelings of inadequacy, self-doubt, or lack of self-worth stemming from early negative experiences.
- Sleep Disturbances. Having trouble falling asleep, experiencing nightmares, or waking frequently due to anxiety or unresolved trauma.
- Chronic Anxiety or Depression. Feeling constantly sad, hopeless, or excessively worried, often as a lingering impact of trauma.
- Avoidance Behaviors. Avoiding people, places, or situations that trigger painful memories or emotions.
- Difficulty Concentrating. Struggling to focus, being easily distracted, or frequently forgetting things due to heightened stress levels.
- Physical Symptoms. Experiencing unexplained physical issues like headaches, stomachaches, or chronic pain linked to emotional stress.
5 Signs of Emotional Trauma in Adults
Here are the signs of emotional trauma in adults:
- Mood swings. Rapid shifts in mood, often unrelated to the situation.
- Feeling of guilt or shame. Persistent negative beliefs about oneself.
- Social withdrawal. Avoiding interactions or becoming isolated.
- Fear of intimacy. Difficulty opening up to others or maintaining closer relationships.
- Physical symptoms. Headaches, chest pain, or gastrointestinal issues with no medical cause.
The Most Common Types of Trauma
Here are the most common types of trauma:
Now, it’s important to note that each type of trauma impacts you differently and may require tailored support or interventions – there’s a different healing process for each trauma.
(And it varies from person to person, too.)
1. Physical Trauma
- Acute injuries. Caused by accidents, falls, sports injuries, or violence (e.g., fractures, burns, wounds).
- Chronic injuries. From repetitive strain or overuse (e.g., carpal tunnel, joint degeneration).
- Blunt force trauma. Injuries caused by impact without penetration (e.g., contusions, internal organ damage).
- Penetrating trauma. Injuries caused by objects piercing the body (e.g., stab wounds, gunshot wounds).
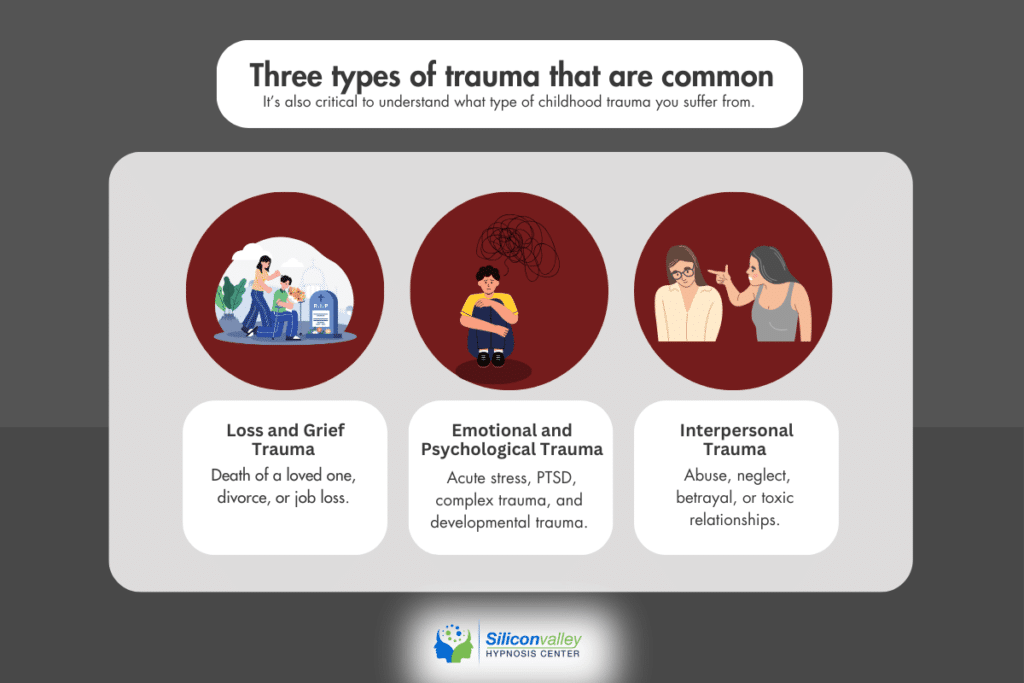
2. Emotional and Psychological Trauma
- Acute stress. A reaction to a single distressing event (e.g., an accident, assault).
- Complex trauma. Exposure to multiple, prolonged, or repetitive traumatic events (e.g., childhood abuse, domestic violence).
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Psychological effects following a traumatic event (e.g., flashbacks, anxiety, nightmares).
- Developmental trauma. Trauma experienced during formative years, affecting emotional and social development (e.g., neglect, childhood abuse).
3. Medical Trauma
Trauma caused by medical procedures, illnesses, or hospitalization (e.g., surgery complications, chronic illness diagnosis).
4. Sexual Trauma
Trauma resulting from sexual assault, abuse, or exploitation.
5. Interpersonal Trauma
Caused by relational issues such as abuse, neglect, or betrayal by a close individual (e.g., domestic violence, toxic relationships).
6. Secondary or Vicarious Trauma
Trauma experienced by witnessing or hearing about another person’s traumatic experience (common in caregivers or first responders).
7. Natural Disaster Trauma
Trauma caused by events like hurricanes, earthquakes, floods, or wildfires.
8. War or Conflict-Related Trauma
Trauma resulting from combat, terrorism, or living in a war zone (e.g., displacement, violence exposure).
9. Loss and Grief Trauma
Trauma due to significant loss, such as the death of a loved one, divorce, or losing a job.
10. Systemic or Collective Trauma
Trauma affecting large groups due to systemic oppression, racism, or genocide.
How to Resolve a Childhood Trauma with Hypnosis?
Hypnosis involves a deep relaxation state that helps you access the subconscious mind and process difficult emotions from childhood trauma in a safe, controlled way. This can reduce symptoms like silent anxiety attacks and rebuild your sense of self.
Here are several ways how hypnosis can help with childhood trauma.
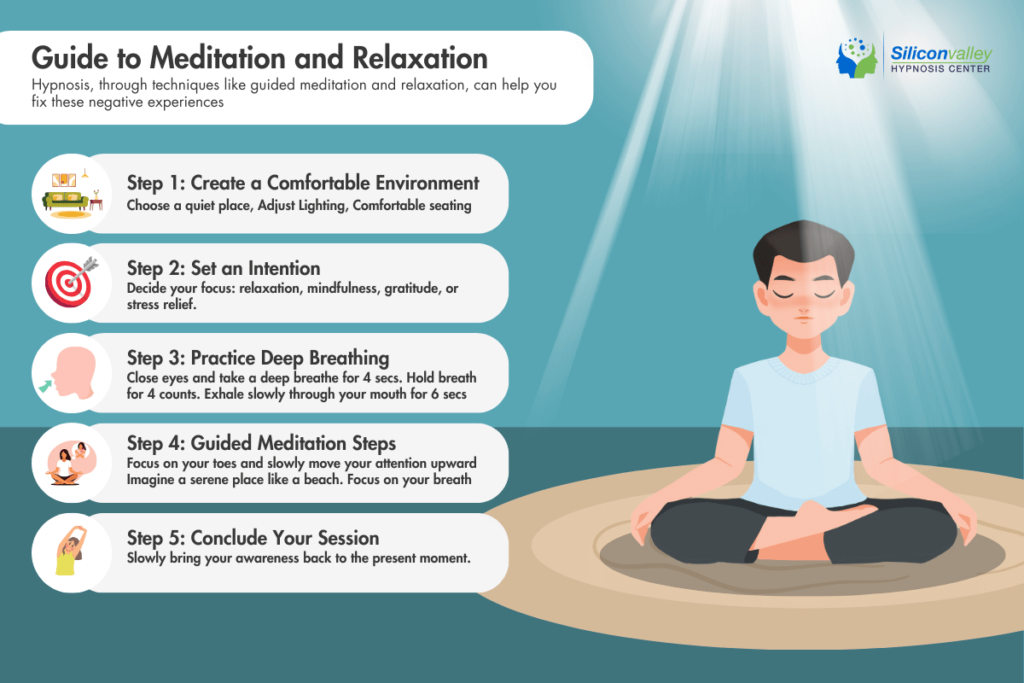
Deep Relaxation and Emotional Processing
Hypnosis gets you to a state of deep relaxation, where you can process difficult emotions in a safe and controlled environment.
This helps you detach from traumatic memories associated with trauma…
…and begin to understand them better.
Reframing Negative Beliefs
Hypnosis lets you identify and reframe negative beliefs and replace them with more positive ones. So, if you believe you’re unworthy, for example, hypnosis can help.
Reduced Trauma Symptoms
People who suffer painful memories and trauma often experience symptoms like:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Flashbacks
- Nightmares
Hypnosis, through techniques like guided meditation or visualization and relaxation, can help you neutralize these negative experiences (or at least reduce them).
Dissociation and Memory Issues
Childhood trauma can also lead to dissociation (feeling disconnected from yourself or your surroundings) or repressed memories.
Hypnosis can be used as a regression therapy and help you process these memories…
…in a safe and therapeutic way.
However, this should be done only with a qualified professional who specializes in trauma therapy and hypnosis.
Building Self-Esteem
Hypnotherapy for childhood trauma can also help with confidence and self-esteem.
Intrusive memories and childhood wounds can significantly damage the way you see and perceive yourself…
…you may feel unworthy of love or see yourself in a bad light.
Either way, hypnotherapy for trauma can get your confidence and self-esteem back on track by helping you focus on your strengths and accomplishments.
Regaining Control
Hypnosis can empower you to take back control of your thoughts and emotions.
By addressing the roots of the trauma, whether it’s sexual abuse, emotional abuse, or an injury, you can develop healthier coping mechanisms — and finally move forward with your life.
Top 5 Hypnosis Techniques for Childhood Trauma
There are five different methods of how hypnosis can help with childhood traumas.
1. Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR)
This technique involves tensing and relaxing different muscle groups of your body.
A hypnotherapist guides you through the process, getting you into a deep state of relaxation, which lets you access and process emotions associated with trauma safely.
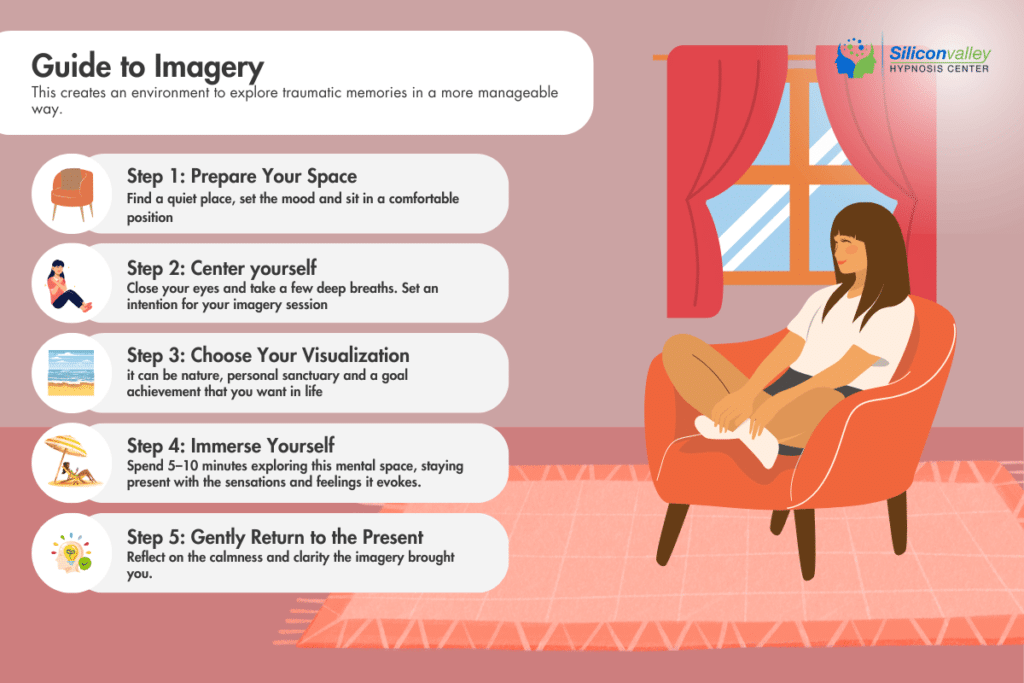
2. Guided Imagery
The therapist guides you through a visualization related to a safe or positive experience, which can often be:
- Calming meadow
- Favorite childhood memory
- Safe and peaceful place
This creates an environment to explore traumatic memories in a more manageable way.
3. Life Regression Therapy
Regression therapy involves revisiting past memories and experiences to gain insight and release emotional blockages. A hypnotherapist guides you back to the time of the trauma, allowing you to process and heal the associated emotions.
But it’s vital to have a safe and supportive environment, and the therapist will guide you back to the present gently after the exploration.

4. Positive Suggestions
Positive suggestions help you develop these powerful tools:
- Healthier coping mechanisms
- Improved self-esteem
- Higher resilience
These suggestions can be incorporated throughout the session to support the overall healing process.
5. Parts Therapy
Parts therapy acknowledges that our psyche is composed of different “parts” with conflicting emotions or beliefs.
With hypnosis, I can help you identify these parts related to your trauma.
Through guided imagery and suggestions, I can help you facilitate communication and potentially integrate these parts, which promotes a sense of wholeness.
Summary: Hypnosis for Childhood Trauma Really Works
Hypnotherapy is an effective therapy that can help with memories of childhood abuse, physical trauma, or life traumas. It lets you access emotions that are deep in your subconscious and conscious mind…
…and minimizes the effects of trauma,bad memories, and their effects today.
To learn more about how hypnosis can help you resolve issues and reach your goals, click below to schedule a consultation session.
FAQ
To break a trauma bond, one must recognize the unhealthy attachment, set firm boundaries, and seek professional therapy or support groups to process the relationship dynamics.
To heal from trauma, focus on therapeutic healing techniques coupled with self-compassion, building a support system, and engaging in practices like mindfulness or EMDR to process and release the emotional pain.
Results vary; some individuals notice improvements after a few sessions, while others require more time depending on the trauma’s complexity.
When conducted by a qualified professional, hypnosis is safe for most people. However, those with certain psychological conditions should consult their healthcare provider first.
Generational trauma refers to the psychological and emotional effects passed down from one generation to the next, often stemming from unresolved traumas such as abuse, neglect, or systemic oppression.